|
|||||||||
|
|
Carbon Cycle
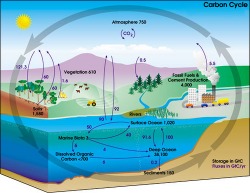
Carbon is one of the basic elements for life on earth. The Carbon Cycle is basically the movement of carbon between the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of the Earth. The Cycle is usually known as the four major reservoirs of carbon by pathways of exchange. These resevoirs are the atmosphere, the terrestrial biosphere, the oceans, and the sediments including fossil fuels. The annual movements of carbon, the carbon exchanges between resevoris, becaus of various chemical, physical, geological, and biological processes. The ocean contains the largest active pool of carbon near the surface of the Earth, but the deep ocean part of this pool does not rapidly exchange with the atmosphere. The order of the Carbon Cycle
Carbon is taken from the atmosphere in several ways, for example, plants perform photosynthesis to convert carbon dioxide into carbohydrates, releasing oxygen in the process. Carbon is released into the atmosphere in several ways, such as, through the respiration performed by plants and animals; this is an exothermic reaction and it involves the breaking down of glucose into carbon dioxide and water. Carbon Dioxide would transfer rates due to photosnthesis and respiration. Carbon is transferre within the biosphere as heterotrophs feed on other organisms or their parts;such as, the uptake of dead organic material by fungi and bacteria for fermentation of decay. Buring of biomass (such as: forest fires, wood used for heating, anything else organic) can also transger substantial amounts of carbon to the atmosphere. In the oceans, Inorganic carbon is carbon compounds with no carbon-carbon or carbon-hydrgogen bonds is improtant in i Different Links
Paragraph. Definitions
Paragraph. Documentation of Sources
http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Library/CarbonCycle/ |
||||||||
|
|
|||||||||